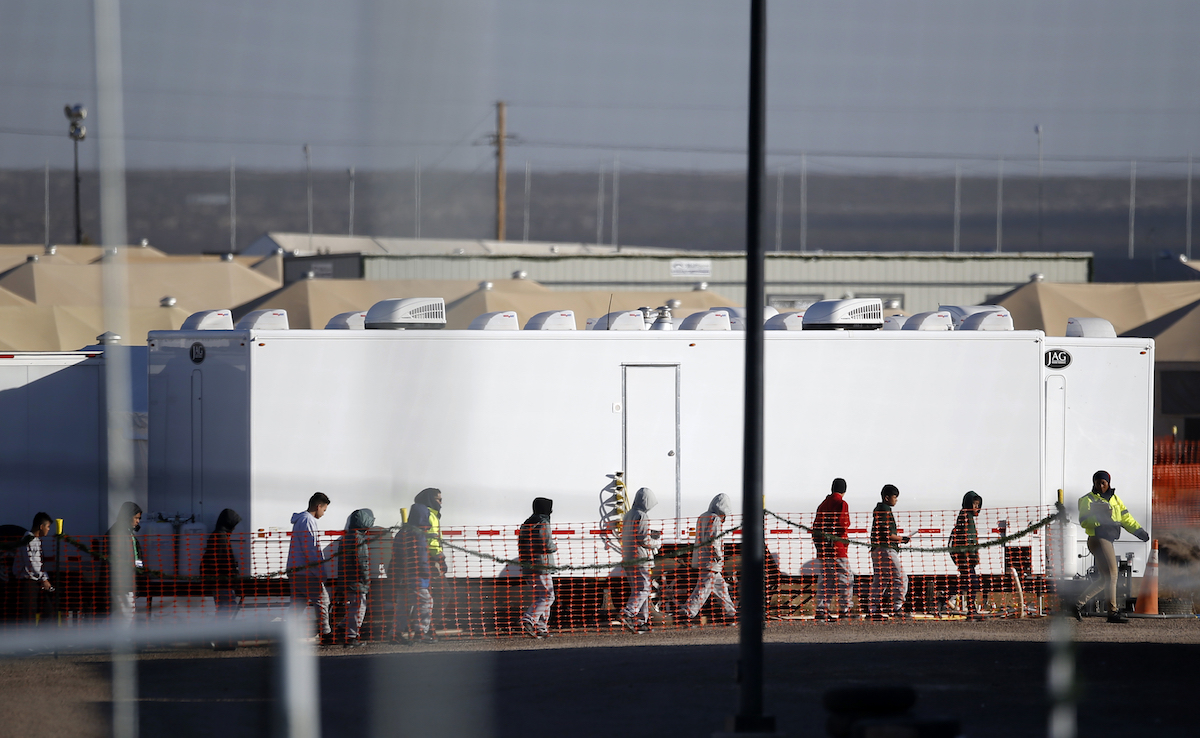
Teen migrants walk in line inside the Tornillo detention camp in Tornillo, Texas, Thursday December 13, 2018. The Trump administration announced in June 2018 that it would open the temporary shelter for up to 360 migrant children in this isolated corner of the Texas desert. Less than six months later, the facility has expanded into a detention camp holding thousands of teenagers, showing every sign of becoming more permanent. (AP Photo/Andres Leighton)
By Garance Burke and Martha Mendoza, Associated Press
Decades after the U.S. stopped institutionalizing kids because large and crowded orphanages were causing lasting trauma, it is happening again. The federal government has placed most of the 14,300 migrant toddlers, children and teens in its care in detention centers and residential facilities packed with hundreds, or thousands, of children.
As the year draws to a close, some 5,400 detained migrant children in the U.S. are sleeping in shelters with more than 1,000 other children. Some 9,800 are in facilities with 100-plus total kids, according to confidential government data obtained and cross-checked by The Associated Press.
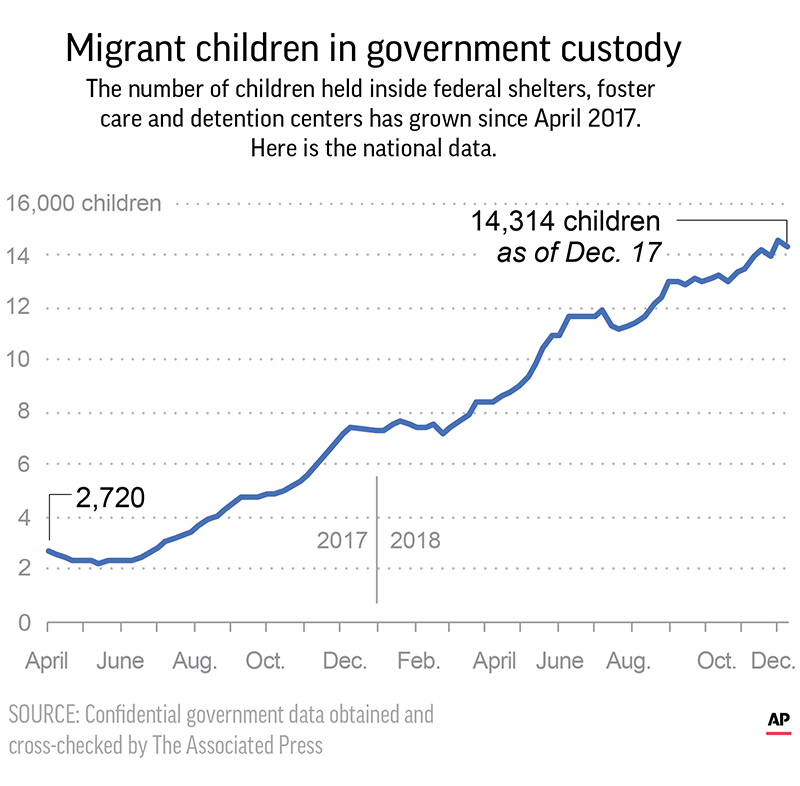

Chart shows number of children at federal shelters.
That’s a huge shift from just three months after President Donald Trump took office, when the same federal program had 2,720 migrant youth in its care; most were in shelters with a few dozen kids or in foster programs. Some of the children may be released sooner than anticipated, because this week the administration ended a portion of its strict screening policies that had slowed the placement of migrant kids with relatives in the U.S.
Until now, public information has been limited about the number of youths held at each facility overseen by the Office of Refugee Resettlement, even for attorneys representing the kids. But the AP obtained data showing the number of children in individual detention centers, shelters and foster care programs for nearly every week over the past 20 months, revealing in detail the expanse of a program at the center of the Trump administration’s immigration crackdown.
The data shows the degree to which the government’s approach to migrant youth has hardened, marking a new phase in a federal program originally intended to offer safe haven to vulnerable children fleeing danger across the globe. It’s been taking at least twice as long —on average two months rather than one— for youth held inside the system to get out, in part because the Trump administration added more restrictive screening measures for parents and relatives who would take them in.
That changed Tuesday when the administration ended a policy requiring every adult in households where migrant children will live to provide the government with fingerprints. All still must submit to background checks, and parents themselves still need to be fingerprinted. Nonetheless, officials said they could now process some children more rapidly, and hoped to shorten shelter stays that had dragged on so long kids sometimes wondered if their parents had abandoned them for good.
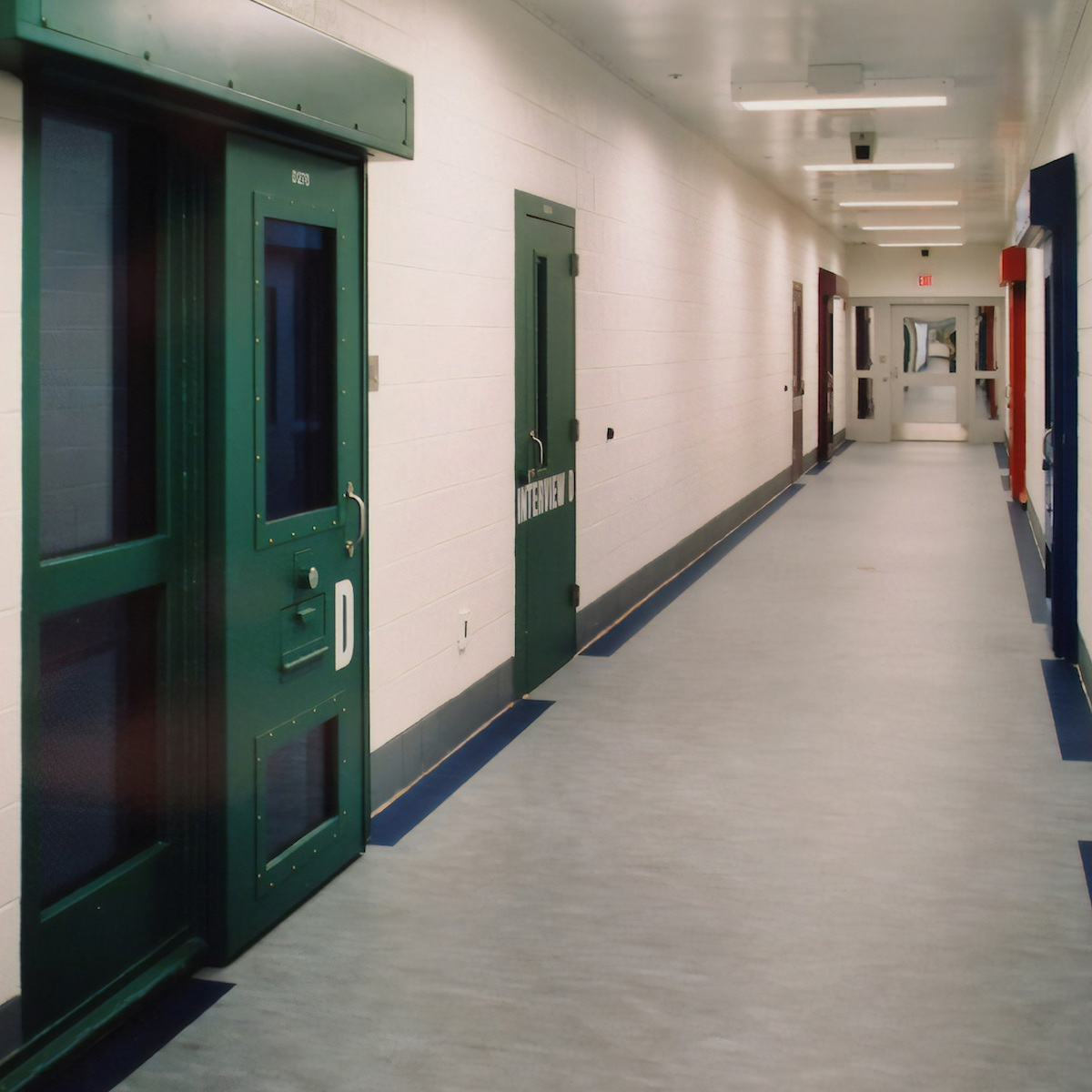


This image provided by the Shenandoah Valley Juvenile Center shows part of the interior of the building in Staunton, Va. Immigrant children as young as 14 housed at the juvenile detention center say they were beaten while handcuffed and locked up for long periods in solitary confinement, left nude and shivering in concrete cells. The abuse claims are detailed in federal court filings that include a half-dozen sworn statements from Latino teens jailed there for months or years. (Shenandoah Valley Juvenile Center via AP)
“It’s a pain we will never get through,” said Cecilio Ramirez Castaneda, a Salvadoran whose 12-year-old son, Omar, was taken from him when they were apprehended in June under the administration’s “zero tolerance” policy, which led to nearly 3,000 children being separated from their families. Omar feared his father had given up on him during the five months he spent in a Southwest Key shelter in Brownsville, Texas, with dozens of kids.
Ramirez Castaneda was reunited with Omar last month only to learn that his son had been hospitalized for depression and medicated for unclear reasons and suffered a broken arm while in government custody.
“It’s a system that causes irreparable damage,” he said. “My son says they would tell him that because he wasn’t from here, he had no rights.”
Experts say the deep anxiety and distrust children suffer when they’re institutionalized away from loved ones can cause long-lasting mental and physical health problems. It’s dangerous for all but worse for younger children, those who stay more than a few days and those who are in larger facilities with less personal care.
“This is not a perplexing scientific puzzle. This is a moral disaster,” said Dr. Jack Shonkoff, who heads Harvard University’s Center on the Developing Child. “There has to be some way to communicate, in unequivocal terms, that we are inflicting punishments on innocent children that will have lifelong consequences. No matter how a person feels about immigration policy, very few people hate children, and yet we are passively allowing bad things to happen to them.”
Administration officials said increased need has driven them to expand the number of beds available for migrant children from 6,500 last fall to 16,000 today. Mark Weber, a spokesman for the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, which oversees ORR, said sheltering children in large facilities, while not preferable, is a better alternative than holding them for long periods at Border Patrol stations ill-suited to care for them.
“This is an amazing program with incredibly dedicated people who are working to take care of these kids,” he said. “There are a large number of children and it’s a difficult situation, and we are just working hard to make sure they are taken care of and placed responsibly.”
Weber confirmed a number of specific shelter populations from the data the AP obtained. To further verify the data, reporters contacted more than a dozen individual facilities that contract with ORR to house migrant children. Reporters also cross-referenced population numbers previously collected by AP and its partners.
The kids in government care range in age from toddlers to 17. The vast majority crossed the border without their parents, escaping violence and corruption in Central America, but some were separated from their families at the border earlier this year.
The care they receive varies greatly in the opaque network, which has encompassed 150 different programs over the last 20 months in 17 states. Some children live with foster families and are treated to Broadway shows, while others sleep in canvas tents exposed to the elements amid the Texas desert.
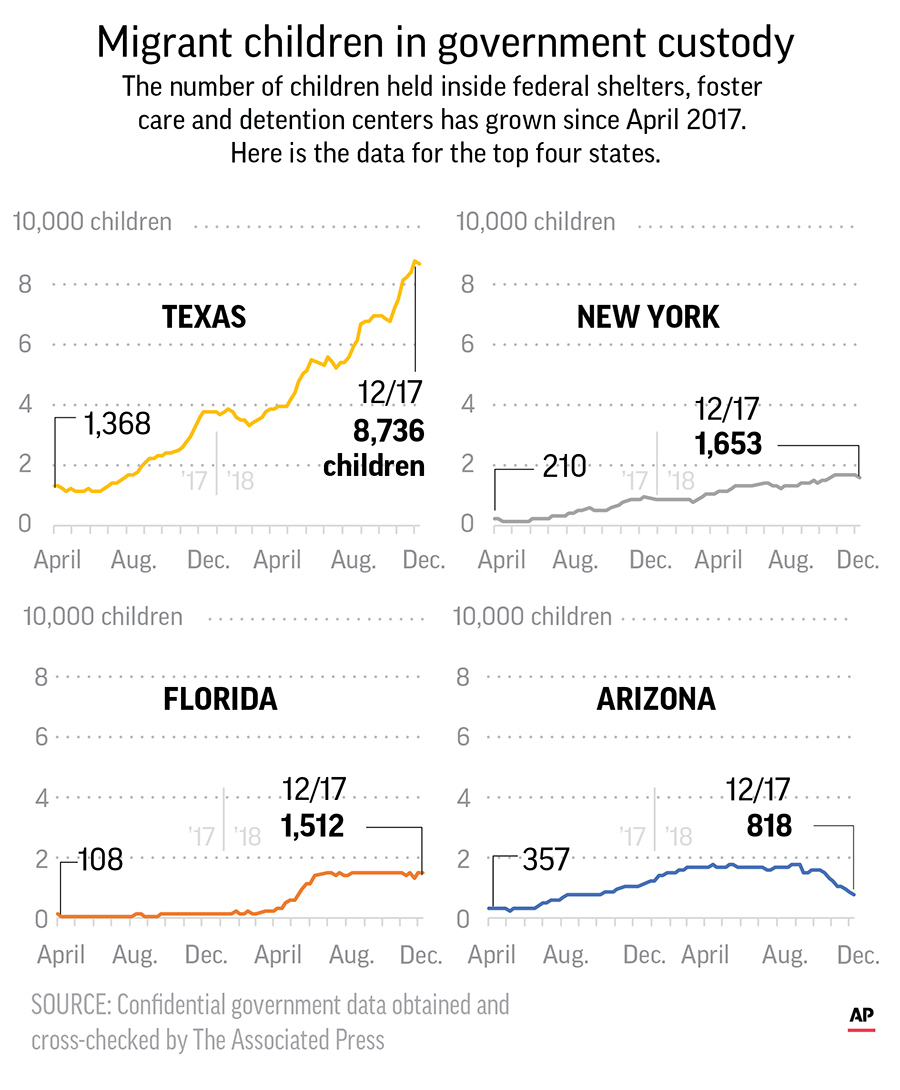

The number of children held inside federal shelters, foster care and detention centers has grown since April 2017. Here is the data for the top four states:
Through dozens of interviews and data analysis, AP found:
- As of December 17, some 9,800 children were in facilities housing more than 100 kids; 5,405 of those were in three facilities with more than 1,000 youths—two in Texas and one in Florida.
- Texas had the most growth over the last 20 months in the number of kids under ORR custody. In April 2017, there were 1,368 migrant children in facilities or foster care in Texas. As of Dec. 17, the number was about 8,700.
- New York had the second-highest number of children: 1,653, up from 210 in April 2017. Cayuga Centers grew from about 40 kids to close to 900; all are in foster homes.
- The five largest providers, in order, are Austin, Texas-based Southwest Key; San Antonio-based BCFS Health and Human Services; Comprehensive Health Services Inc., based in Cape Canaveral, Florida; Cayuga Centers in Auburn, New York; and Chicago-based Heartland Alliance. Together they had about 11,600 children—or more than 80 percent of the 14,314 migrant youth in ORR custody as of December 17.
- The states with children in care are: Arizona, California, Connecticut, Florida, Illinois, Kansas, Massachusetts, Maryland, Michigan, New Jersey, New York, Oregon, Pennsylvania, South Carolina, Texas, Virginia and Washington state.
Kids continue to enter the system, though dozens of the care providers have been sued or disciplined before for mistreating children in their care. Now new litigation is piling up as attorneys fight to get migrant children released.
Staff members at a Southwest Key shelter in Phoenix allegedly physically abused three children this year, leading to the closure of the shelter in October, federal officials said. And a lawsuit filed earlier this year alleged that Latino youths at the Shenandoah Valley Juvenile Center in Virginia were beaten while handcuffed and locked up for long periods in solitary confinement, left nude and shivering in concrete cells.
The American Academy of Pediatrics and many experts warn against institutionalizing children in large groups. Dr. Ryan Matlow, a Stanford clinical psychologist whose work addresses the impact of early life stress, said best practices minimize the number of children in any one shelter.
“Children are being treated as cogs in a machine, and their individual backgrounds, interests and unique identities are devalued as they are lost amongst the masses. This experience then becomes internalized, with significant psychological consequences,” said Matlow, who recently met with migrant children in custody. “There is no way in which a mass detention setting can replicate the experience and support that comes from family and community.”
The number of migrant children caught by immigration officials and then turned over to the Office of Refugee Resettlement has dropped under Trump: there were 49,100 in fiscal year 2018 compared to a high of 59,170 in fiscal year 2016, when a surge of youth crossing the border prompted the Obama administration to open emergency shelters at military bases. The average length of stay has increased, however, from about 34 days in January 2016 to around 60 days , according to government reports. In October, the average length of stay reached 89 days, according to data HHS provided to members of Congress, who shared it with AP.
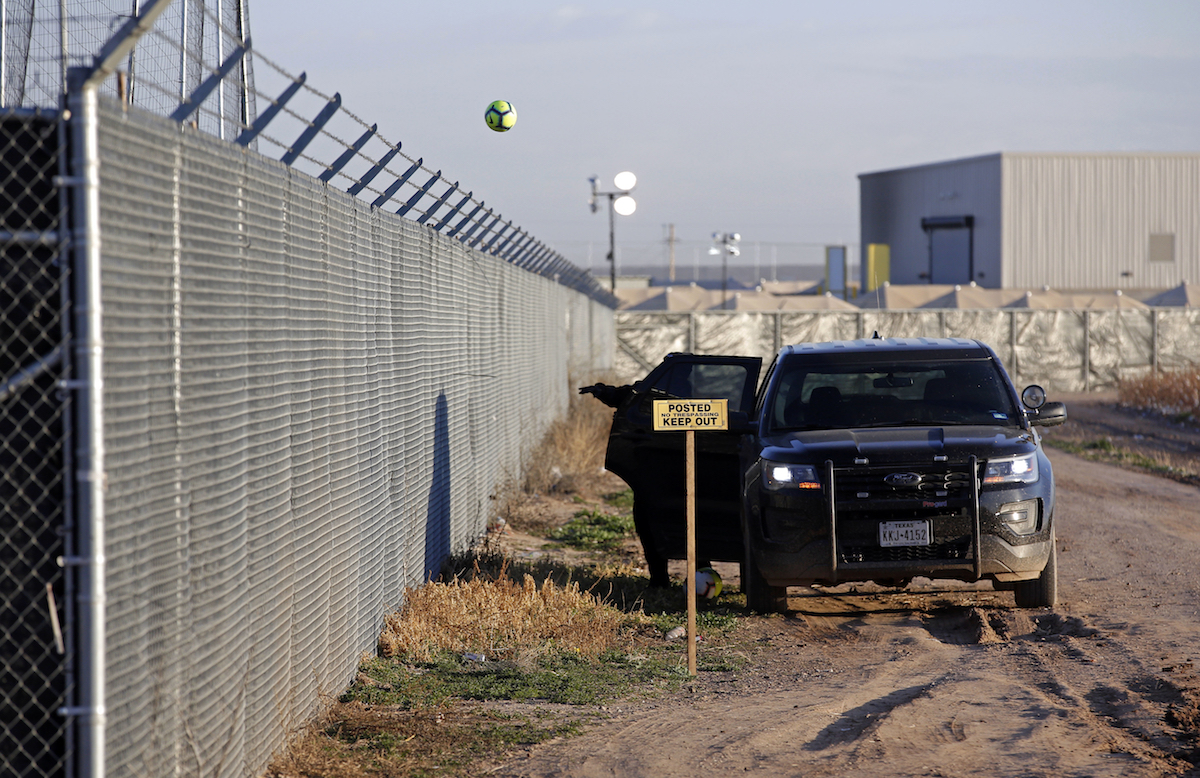


A private security guard throws a soccer ball back inside the Tornillo detention camp for migrants in Tornillo, Texas, Thursday December 13, 2018. (AP Photo/Andres Leighton)
Earlier this year, the Trump administration added new screening requirements that made it harder for parents and other relatives to get approved to take custody of the migrant children—including the fingerprint policy. That information has been shared with Immigration and Customs Enforcement, resulting in the arrests of dozens of would-be sponsors.
Under this week’s change, only a parent or individual directly responsible for a child will have to submit fingerprints.
HHS spokesman Weber said some fingerprinting requirements were necessary to ensure children are released to a safe environment: “Given the multitude of bad actors around the children, you really have to be careful.”
The ORR migrant children’s program has already cost taxpayers more than $1.5 billion, according to federal grant disclosures. Another $1.1 billion has been requested as part of the 2019 budget.
The facilities housing these children range from bucolic to jail-like.
In a Baltimore suburb, Board of Child Care shelters about 50 migrant children amid 28-acres of cottages and grassy lawns; Rite of Passage in Arizona has about 100 kids sheltered at facilities that look like posh, private schools surrounded by trees and fields. Youth for Tomorrow, founded in Bristow, Virginia, by former Washington Redskins coach Joe Gibbs to serve troubled teens, is housing about 110 migrant kids on its 215-acre campus with soccer fields and volleyball courts, music and art therapy.
Suspected gang members can be sent to several high-security facilities. An attorney for a Guatemalan teen held in the Yolo County, California, juvenile detention center for 11 months said his client was locked in restraints when he acted out and stung with pepper spray. Attorney Travis Silva convinced a judge to release the boy in November to his mother in Ohio. He’s now being treated for trauma and mental illness, said Silva, and shelter statistics show 14 other teens remain locked inside.
“He was locked in a cell, allowed one hour a day outside,” said Silva. “And outdoor time was anxiety-provoking, because that’s when there could be fights.”
At Tornillo, Texas —the largest of all the facilities— some 2,745 teens are held in massive tents. Staff aren’t allowed to touch them, except for fist bumps. They can’t hug.
“The programs vary wildly from place to place,” said Shana Tabak, who directs the Atlanta office of the Tahirih Justice Center, which represents immigrant women and girls. “The federal government has taken a haphazard approach to caring for these human beings.”
Republican Congressman Will Hurd, whose district includes Tornillo, demanded that the government reunite the children with their families and shut down the detention camp by the end of the year, when the contract expires.
“Unnecessarily holding children for prolonged periods of time is no deterrent to illegal immigration,” he said. “All of this is a symptom of a broader problem, and that is that we’re not doing enough to address root causes of migration. We are the United States. We are better than this.”
Every kid comes with their own set of needs, many severe.
“We mostly have housed teenagers, some with their babies, and some sibling pairs whose parents have been murdered,” said Regina Moller, executive director of Noank Community Support Services in Groton, Connecticut. Noank can house up to 12 of the kids at a time and has been at or near capacity for weeks now.
Abbott House in Irvington, New York, takes kids with medical needs such as diabetes, cerebral palsy, depression and anxiety. It is housing 51 migrant boys and girls; the youngest is 3 years old, said medical director Dr. Luis Rodriguez.
A handful of boys are getting therapeutic intervention for sexual behavior or mental health issues at Friends of Youth in Seattle. “Most of these children are coming from great trauma and really terrible things have happened to them in their short lives,” said president Terry Pottmeyer. “They respond so positively, we see incredible results.”
This December, many will be enduring their first holidays without family.
Manuel Marcelino Tzah, a Guatemalan father whose 12-year-old daughter, Manuela, was taken from him and held in a Southwest Key facility in Houston for nearly two months, said his family is still processing the pain of separation and detention.
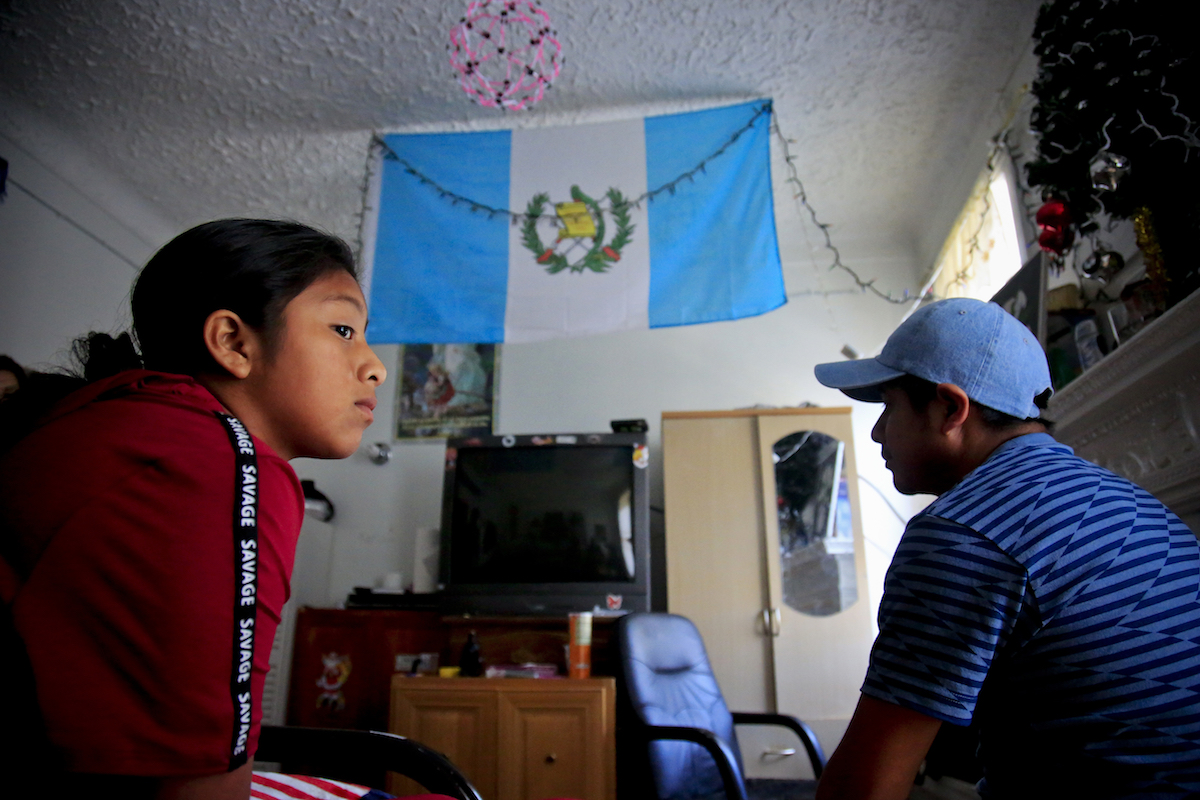


Manuela Adriana, 11, left, sit with her father Manuel Marcelino Tzah inside their apartment hours after her release from immigrant detention, Wednesday July 18, 2018, in Brooklyn borough of New York. The Guatemalan asylum seekers were separated May 15 after they crossed the U.S. border in Texas. (AP Photo/Bebeto Matthews)
“She’s doing OK now; she is going to school and learning some English,” said Marcelino Tzah, whose immigration case is pending in a New York court near his new home in Brooklyn. “We really went through some difficult times, and sometimes she remembers it and is hit with the sadness of it. I tell her what happened, happened, and now we are here and struggling for a better life.”
Associated Press data journalist Larry Fenn and reporter Jennifer Peltz in New York contributed to this report.
Follow @garanceburke and @mendozamartha on Twitter.