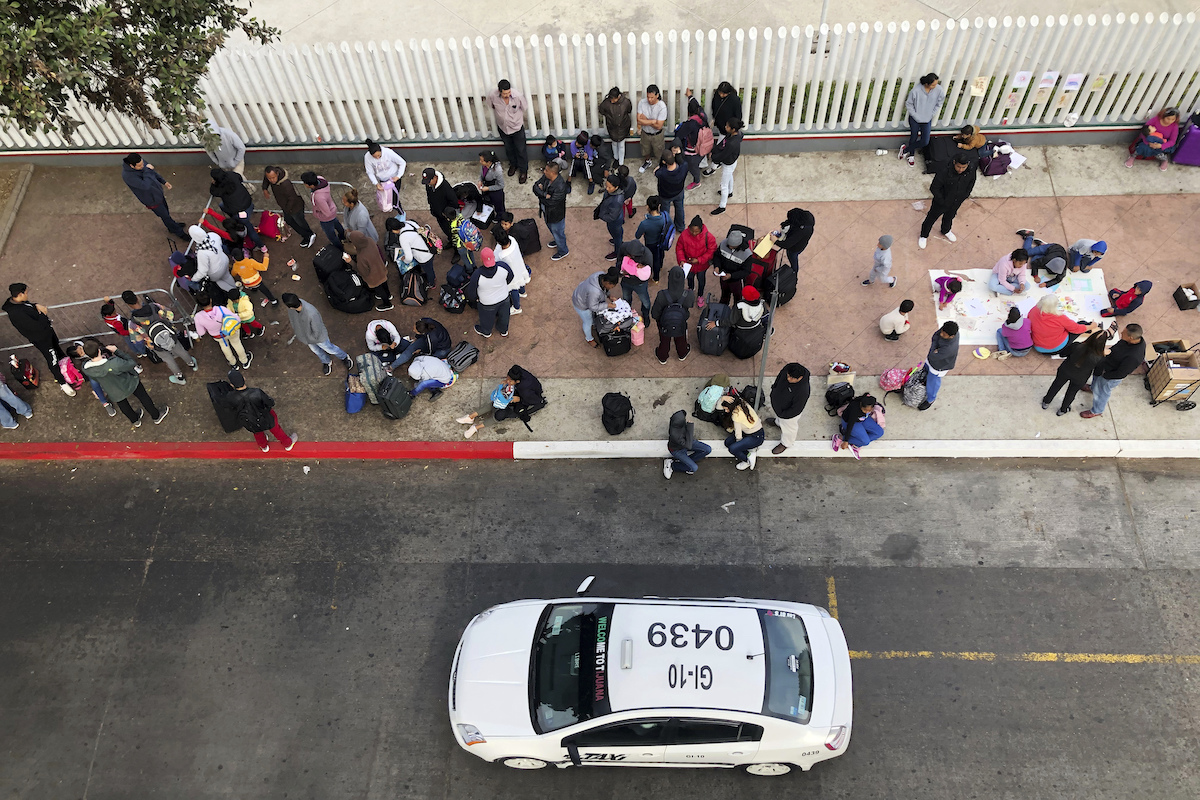
In this Nov. 10, 2019, file photo, migrants gather at the U.S.-Mexico border in Tijuana, Mexico, to hear names called from a waiting list to claim asylum in the U.S. (AP Photo/Elliot Spagat, File)
By ELLIOT SPAGAT, Associated Press
SAN DIEGO (AP) — The Trump administration on Wednesday proposed sweeping restrictions on asylum, seeking to align a legal framework with the president’s efforts to limit immigration to the United States.
The moves are only the latest in a series of measures that Trump has taken to limit asylum—this time aimed at changing complicated guidelines and procedures governing immigration courts.
The changes, outlined in 150 pages of legalese, aim to redefine how people qualify for asylum and similar forms of protection to prevent them from being persecuted or tortured if sent home.
Judges will be allowed to dismiss cases without court hearings if supporting evidence is determined to be too weak. Rules will define when a claim may be declared “frivolous” and raise the threshold for initial screenings under the United Nations Convention Against Torture.
The administration will propose new definitions for some ways people qualify for asylum, specifically “political opinion” and membership in a “particular social group.”
Asylum is for people who face persecution for their race, religion, nationality, political opinion or membership in a social group, a loose category that may include victims of gang or domestic violence. Narrowing those ways to qualify would mean more rejected claims.
The Justice and Homeland Security departments said asylum-seekers who clear initial screenings will have claims heard by an immigration judge in “streamlined proceedings,” according to a brief press release, replacing longstanding rules in immigration law.
Since the U.S. became the world’s top destination for asylum-seekers in 2017, the Trump administration has made multiple attempts to make it harder to get, asserting that the system is rife with abuse.
The Justice and Homeland Security departments said the changes would bring more efficiency to a system with an immigration court backlog of more than 1.1 million cases.
The rules will “more effectively separate baseless claims from meritorious ones,” the departments said. “This would better ensure groundless claims do not delay or divert resources from deserving claims.”


President Donald Trump speaks during a roundtable discussion with African-American supporters in the Cabinet Room of the White House, Wednesday, June 10, 2020, in Washington. (AP Photo/Patrick Semansky)
Critics swiftly condemned the measure. Aaron Reichlin-Melnick, policy counsel for the American Immigration Council, said it was much more far-reaching than Trump’s previous attempts to curb asylum and “would lead to the denial of virtually every claim except a lucky few.”
“The proposed changes would represent the end of the asylum system as we know it,” he said.
Details are expected to be published in the Federal Register on Monday with 30 days for public comment before they take effect. Lawsuits may delay or derail the effort.
The administration effectively put asylum out of reach for many people at the Canadian and Mexican borders in March under a 1944 public health law aimed at preventing spread of the coronavirus, but that move is described as temporary. It allows the government to immediately expel people from Mexico and Central America to Mexico without claiming asylum, usually within two hours.