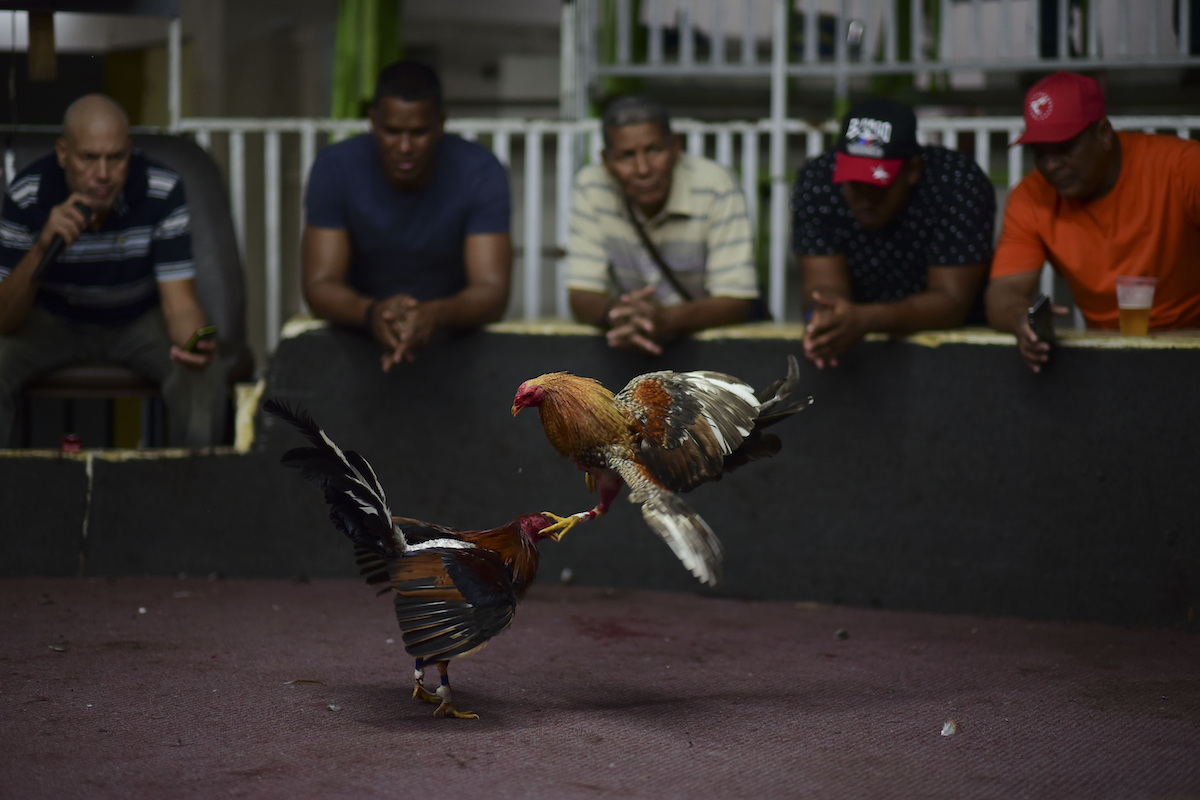
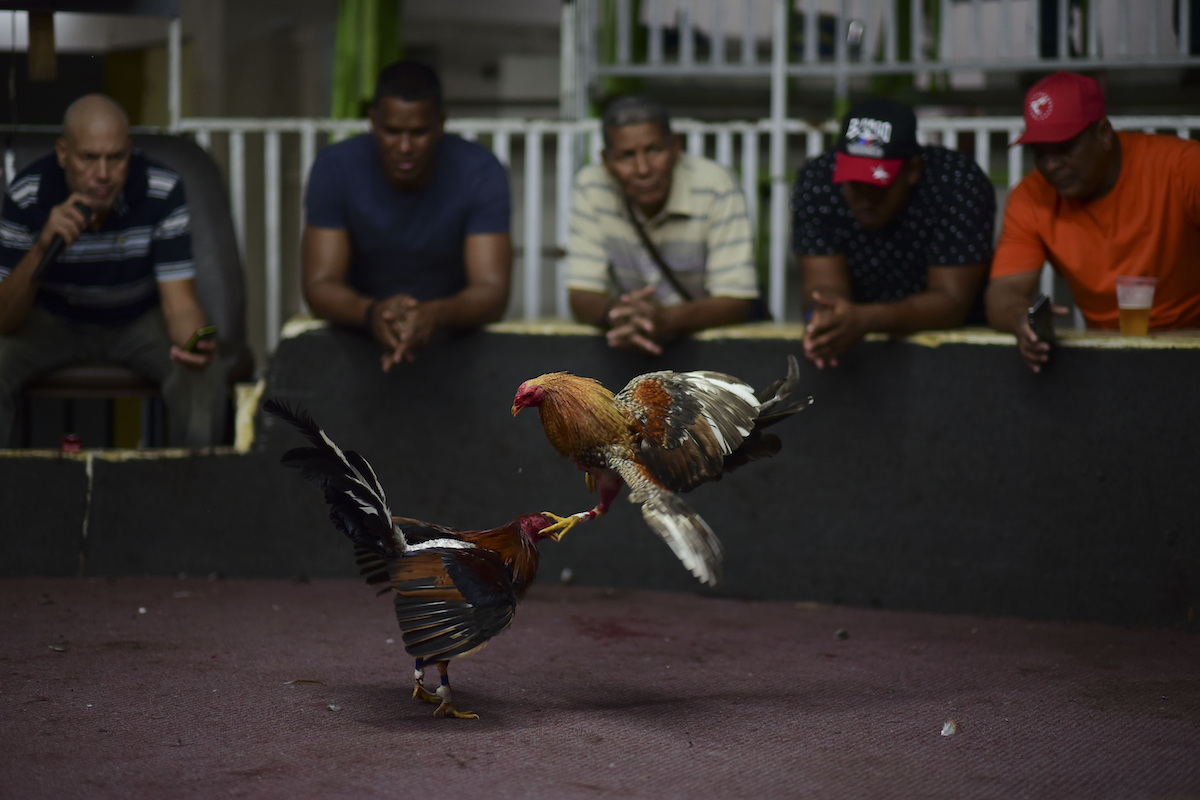
Fight night at the Campanillas cockfighting club, in Toa Baja, Puerto Rico, Wednesday, December 18, 2019. Some Puerto Rico legislators believe the fight over the federal ban on cockfights will end up in court, driving them underground once again. (AP Photo/Carlos Giusti)
By DÁNICA COTO, Associated Press
TOA BAJA, Puerto Rico (AP) — Felipe Espinal walked into his cockfighting establishment Wednesday night in the northern town of Toa Baja and held up a white pen in triumph as he recorded the moment with his cellphone.
The crowd hushed as he cried out: “This is the pen that said we can keep fighting gamecocks!”
Hours earlier, Puerto Rico Gov. Wanda Vázquez signed a bill authorizing cockfighting in defiance of a federal ban that goes into effect Friday. She was surrounded by Espinal and other cockfighters who cheered the decision, some even crying, relieved, if only temporarily, that the island’s 400-year-old tradition was still alive.
“We can now live in peace,” said Tony Rojas, who takes cares of 100 gamecocks for a living. “I’m 65 years old. Who’s going to hire me? Nobody wants me even for cleaning floors. I couldn’t sleep wondering what was going to happen.”
The U.S. territory of 3.2 million people has 71 cockfighting establishments in 45 municipalities licensed by the island’s Department of Sports and Recreation. Officials estimate the industry generates $18 million a year and employs some 27,000 people such as Rojas, noting that jobs range from judges to technicians who clean gamecocks and feed them papaya after fights to those who secure plastic spurs on cocks before every fight.
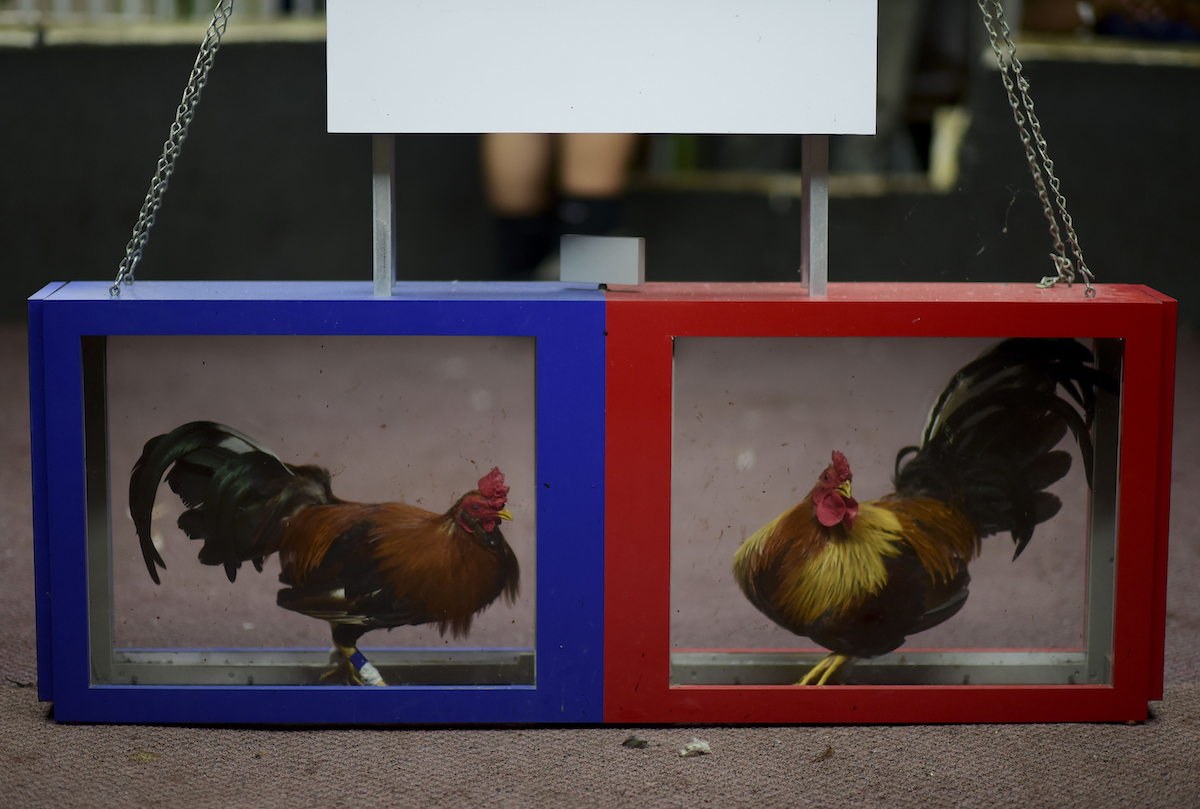


Fight night at the Campanillas cockfighting club, in Toa Baja, Puerto Rico, Wednesday, December 18, 2019. (AP Photo/Carlos Giusti)
Many of them feared for their livelihoods when Congress approved the 2018 Farm Bill last December. It contained the Parity in Animal Cruelty Enforcement Act that aimed to end cockfighting in U.S. territories, giving them one year to comply. The practice was already illegal in all 50 U.S. states but is still widely practiced in other U.S. jurisdictions including Puerto Rico.
The move made many officials in Puerto Rico bristle at what they viewed as another intrusion by the federal government. After all, cockfighting was legalized in 1933 by a Puerto Rico governor from Kentucky who sought to attract U.S. tourists to the island. That move ended 34 years of underground fighting that began when the U.S. government banned the practice in May 1899 after it defeated Spain and occupied Puerto Rico.
It was the Spanish conquistadors who brought cockfighting to Puerto Rico, where it cut through race and social classes, according to documents that local historian Juan Llanes filed in 2014 with the U.S. National Register of Historic Places.
“Through their birds, in the arena, slaves could defeat their masters, blacks could defeat whites, Criollos could defeat Peninsulares,” he wrote.
Cockfighting grew so popular it even prompted a Roman Catholic bishop in 1750 to prohibit cockfights at certain times because church attendance had dropped, Llanes says.
“The gamecock sport in Puerto Rico is not going to disappear,” said Gerardo Mora, executive director of Puerto Rico’s Cockfighting Commission, a part of the island’s Department of Recreation and Sports.
Mora was among the roughly 50 people attending cockfights at Espinal’s establishment Wednesday night in Toa Baja, a town whose first cockfighting arena was founded in 1786.
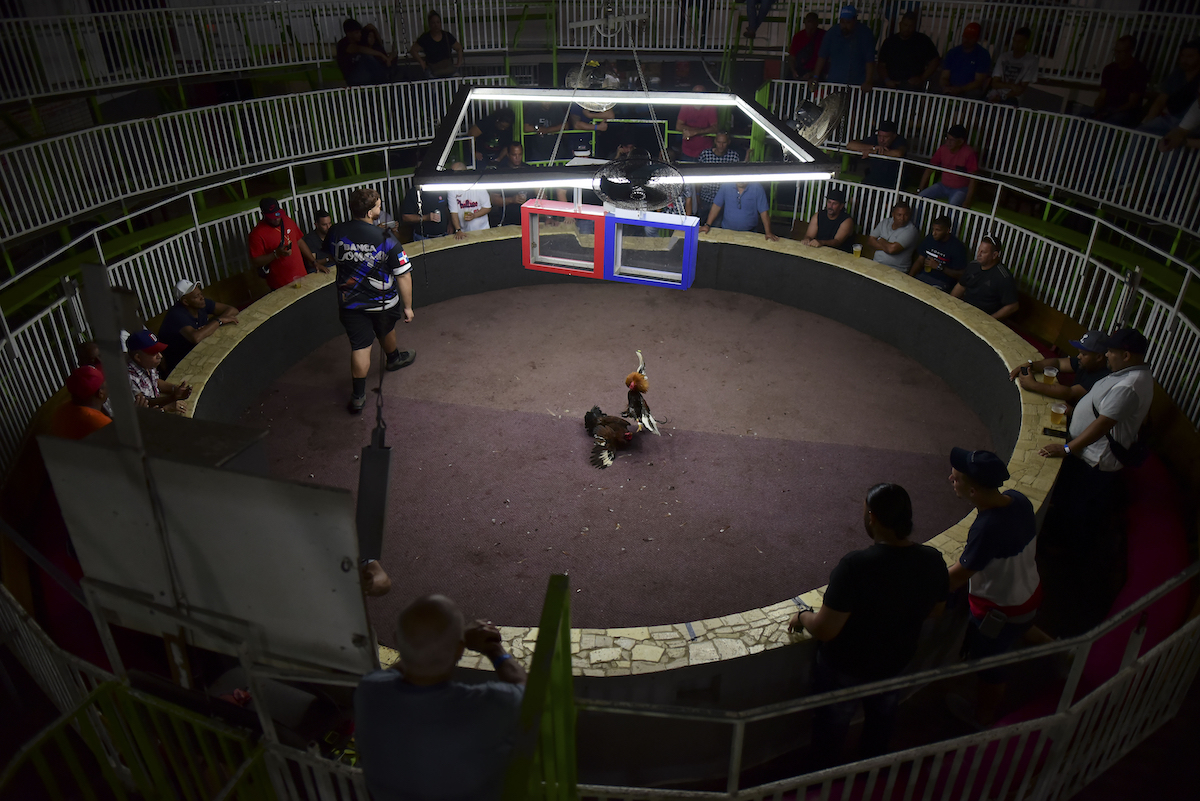


Fight night at the Campanillas cockfighting club, in Toa Baja, Puerto Rico, Wednesday, December 18, 2019. (AP Photo/Carlos Giusti)
Cheers filled the air every time a cock gouged its opponent’s eyes out or stepped on its head in triumph after it collapsed and died following intense battles that lasted less than two minutes. Those that died were thrown into a black plastic bag to be doused with gasoline, set on fire and later buried.
Sitting in the crowd was Yeadealeaucks Báez, a teacher and only one of three women at the event. She works in the kitchen of a nearby cockfighting establishment with her husband, a job she said has allowed them to send their daughter to college in Florida and paid for the education of their son, who is now an engineer.
They feared the federal ban would sink them financially, especially given that Puerto Rico is mired in a 13-year recession as it struggles to recover from Hurricane Maria and tries to restructure a portion of its more than $70 billion public debt load.
“I told my husband we would have to sell water at stoplights,” Báez said.
While cockfighters and government officials in Puerto Rico celebrated the defiance of the federal ban, animal activists like Wayne Pacelle, founder of the Washington-based Animal Wellness Action, lamented the move.
Pacelle said he believes the estimate of cockfighting’s economic impact for Puerto Rico is inflated and dismisses arguments that the activity is a tradition for the island.
“Just because people are enthusiastic about their sport does not mean it’s part of their culture,” he said. “There is something gratuitous about cockfighting that offends the sensibilities of people.”
PETA Latino also rejected the governor’s move, saying it defied modern standards of ethics and compassion. The group accused local government officials of protecting a “cruel industry.”
Some Puerto Rico legislators believe the fight over the island’s effort to avoid the federal ban will end up in court.
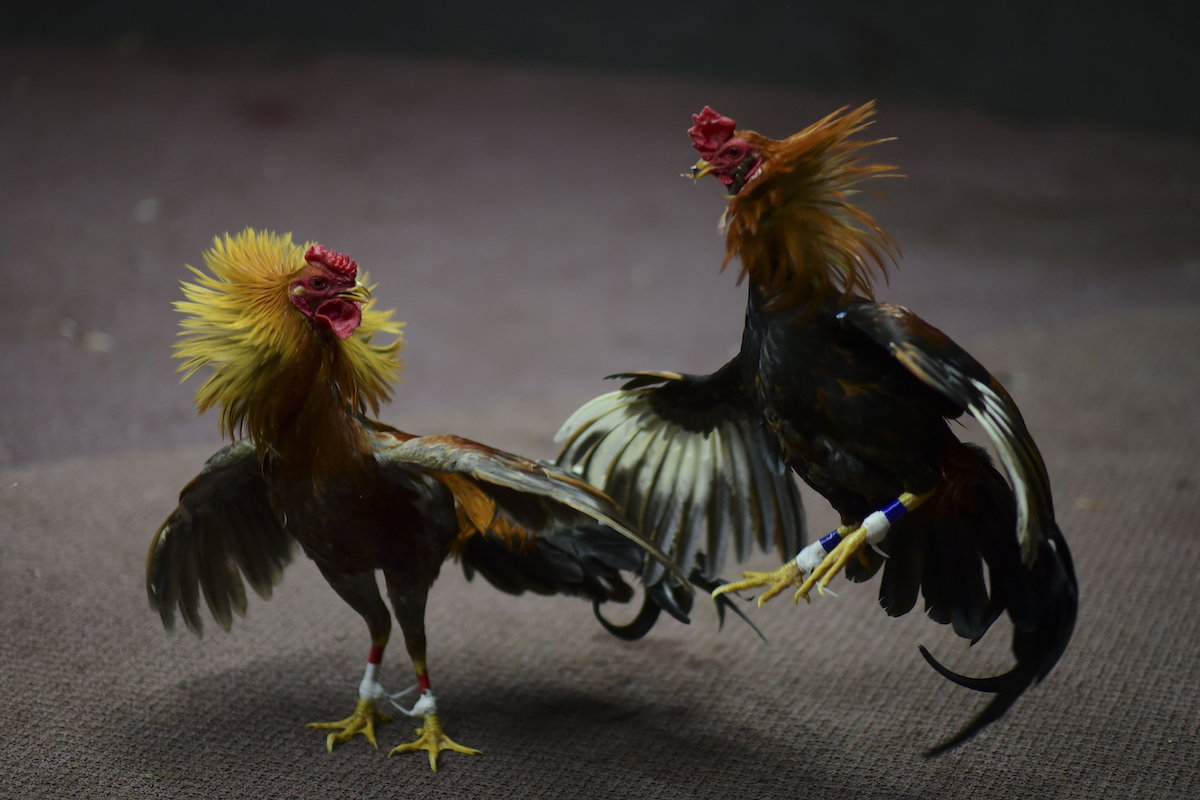


Fight night at the Campanillas cockfighting club, in Toa Baja, Puerto Rico, Wednesday, December 18, 2019. (AP Photo/Carlos Giusti)
And many cockfighting enthusiasts insist a ban would only drive events underground again.
Cockfighters like Sigfredo Rivera vowed to keep participating as much as possible.
“You have no idea how depressed we were,” he said of the federal ban. “I didn’t quit, and I won’t quit.”