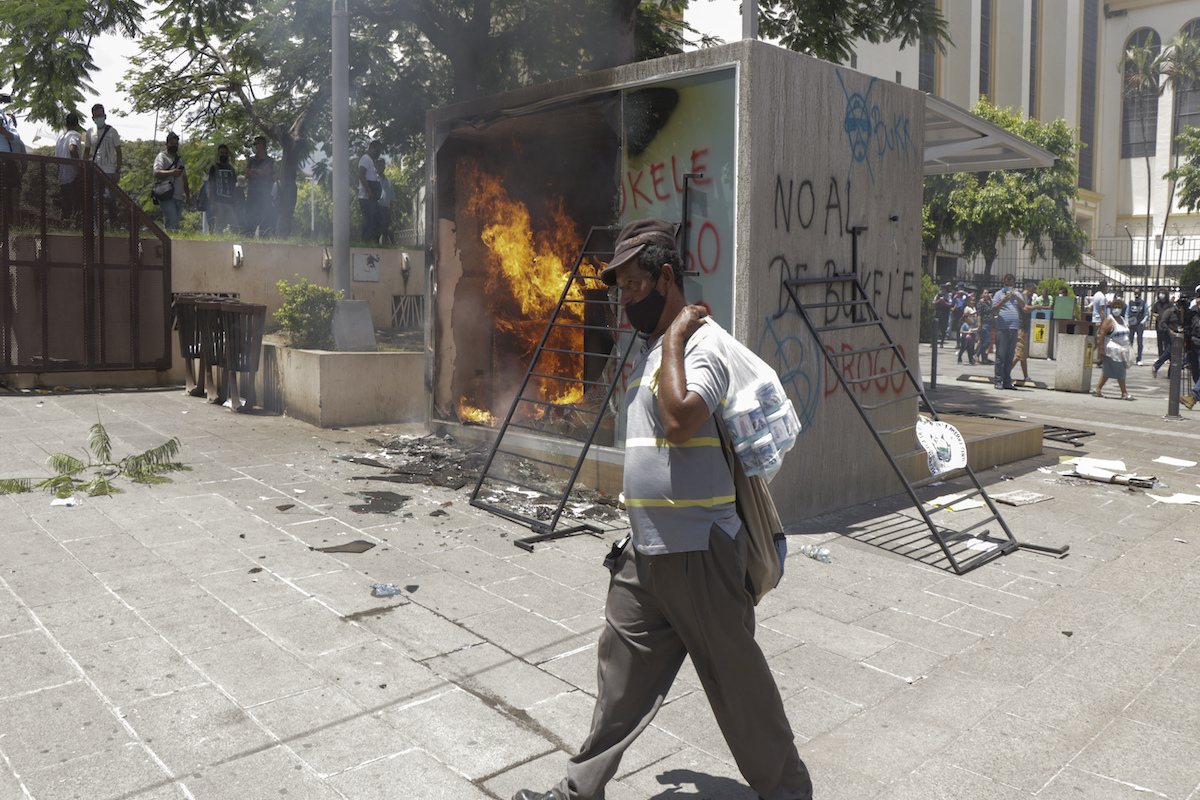
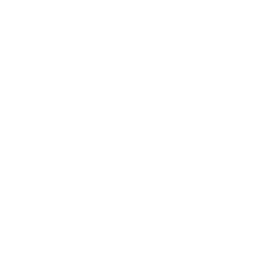
A Chivo digital wallet ATM, which exchanges cash for Bitcoin cryptocurrency, burns after being torched during a protest against President Nayib Bukele in San Salvador, El Salvador, Wednesday, September 15, 2021. Thousands marched against the government of President Bukele, centered on fears Bukele may try for re-election in 2024. (AP Photo/Ivan Manzano)
By MARCOS ALEMÁN, Associated Press
SAN SALVADOR, El Salvador (AP) — Thousands of people gathered in El Salvador’s capital Wednesday for the first mass march against President Nayib Bukele, who protesters say has concentrated too much power, weakened the independence of the courts and may seek re-election.
Some marchers are also protesting the controversial decision by Bukele’s government to make the cryptocurrency Bitcoin legal tender in El Salvador, the first country to do so. Officials rolled out a digital wallet known as the “Chivo” one week ago, but the system has been down frequently for maintenance.
Some marchers wore T-shirts that read “NO To Bitcoin.” A few demonstrators vandalized the special ATM machines set up to handle Bitcoin transactions, but which have been inoperable anyway for much of the week. The cubicle housing one ATM machine was destroyed.
“They say the ‘vandalism’ was the work of ‘infiltrators,’ but there has been vandalism in ALL their demonstrations,” Bukele wrote in his Twitter account. “And why weren’t there any shouts of ‘stop,’ or ‘Don’t do that?’”
Dicen que el “vandalismo” fue hecho por “infiltrados”, pero han hecho vandalismo en TODAS sus manifestaciones ??♂️
Además, ¿por qué no se escuchan gritos de “deténganse” o “no hagan eso”?
Lo que se escucha son APLAUSOS y VÍTORES; y ahí está la prensa. pic.twitter.com/3MetlCntCK
— Nayib Bukele ?? (@nayibbukele) September 15, 2021
The populist president elected in 2019 has maintained high popularity with his vows to stamp out corruption that was rampant among the country’s traditional parties. But some Salvadorans say he is becoming “a dictator” and Wednesday’s march was the first large protest against his government.
“The time has come to defend democracy,” said one of the protesters, former Supreme Court justice Sidney Blanco. “This march is symbolic, it represents weariness with so many violations of the Constitution.”
On the 200th anniversary of Central American independence from Spain, demonstrators have gathered in San Salvador in the largest anti-government protests since President Bukele took office in June of 2019. ?@chelefaro, Cuscatlán Park. pic.twitter.com/H9sB5Ona18
— El Faro English (@ElFaroEnglish) September 15, 2021
Bukele’s New Ideas party won a congressional majority this year and immediately after taking its seats in the National Assembly in May, it replaced the five members of the Constitutional Chamber and the independent attorney general who had balked at several of Bukele’s earlier actions.
Soon after, the Constitutional Chamber tossed aside what had long been interpreted as a constitutional ban on consecutive presidential reelection, setting the stage for Bukele to potentially seek a second term in 2024. Bukele has not so far announced plans to seek reelection, but critics assume he will.
Milton Brizuela, leader of the country’s medical association, said “judicial independence is important to us.”
U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken issued a statement congratulating Central American countries on their shared independence day Wednesday; the region won independence from Spain 200 years ago.
But Blinken warned that “anti-democratic developments pose a growing threat to Central America’s future,” adding “The United States stands with all those speaking truth to power.”
The digital wallet appears to have been overloaded by the sheer number of Salvadorans looking to take advantage of the $30 bonus that the government put in each account to incentivize adoption.
Bukele, the main promotor of using the cryptocurrency, acknowledged the government’s three-month rollout may have been too ambitious. He said technical glitches had prevented the app from working on some kinds of phones.
There has been skepticism about the government’s enthusiastic adoption of bitcoin as a legal tender along with the U.S. dollar since Bukele announced it in a video recorded in English and played at a bitcoin conference in Miami in June. Bitcoin is subject to wild swings in value in a matter of minutes.
Any business with the technological capacity to do so is required to accept payment in bitcoin, but no private citizen is required to use it.
Recent public opinion surveys in El Salvador have said a majority of Salvadorans oppose making it an official currency. Still, Bukele says there are now a half-million users of the digital payment system in the Central American nation.