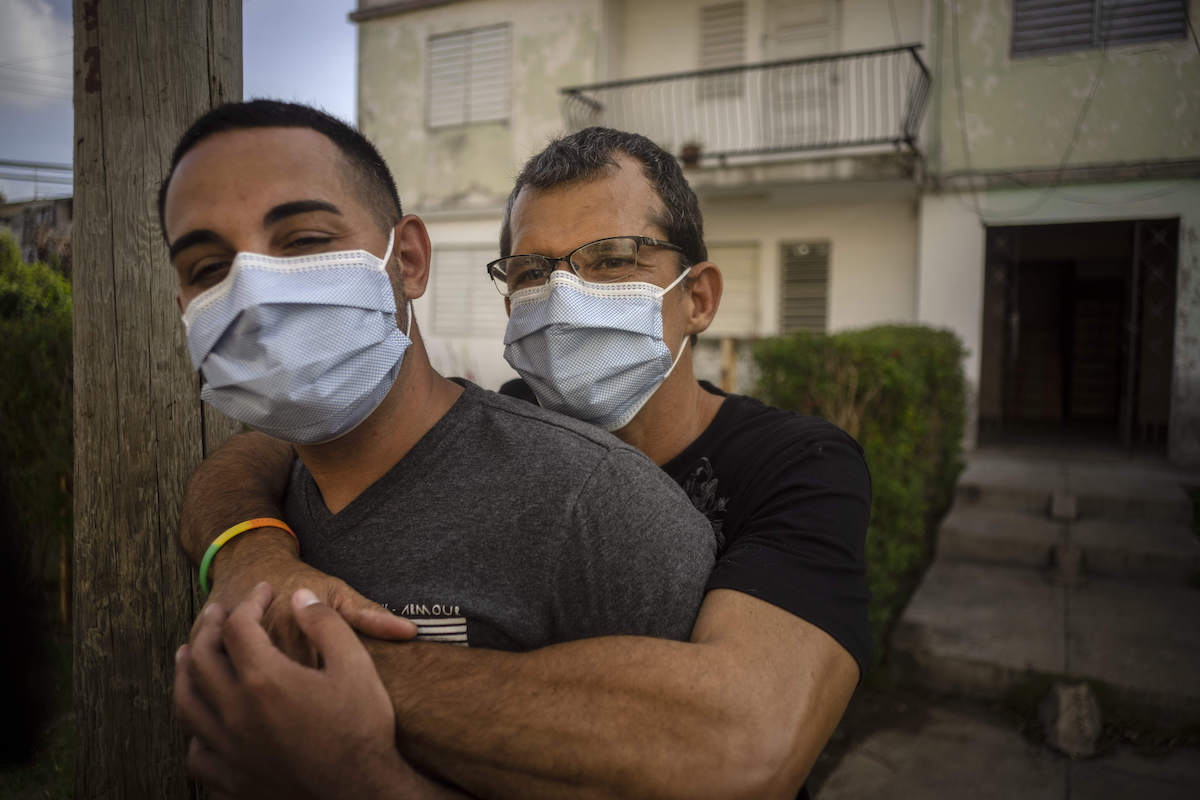
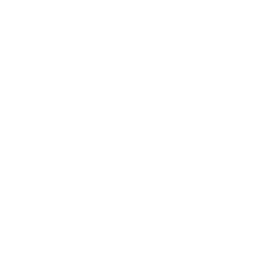
Lázaro “Lachi” González, behind, hugs his partner Adiel González after a video interview outside their home in Matanzas, Cuba, Thursday, October 7, 2021. (AP Photo/Ramón Espinosa)
By ANDREA RODRÍGUEZ, Associated Press
HAVANA (AP) — Adiel and Lachi are anxious to get married, perhaps dressed in black, in a ceremony by the seashore.
The idea bothers the Rev. Moises de Prada, who like many of his parishioners opposes a proposal to legalize same-sex marriage in Cuba.
The socialist government recently published a draft Family Law and asked for public comment ahead of a referendum, creating an unusually public clash over policy on the island where Pentecostal churches have been growing.
For Adiel González, a 31-year-old theologian, the idea of submitting his right to marriage for a public referendum is painful.
“You are submitting to the vote of a heterosexual, heteronormative majority the rights of a minority,” he said from his apartment in the central city of Matanzas, where two cats roam and a cross in the rainbow colors of the gay flag hangs from a wall.
Both he and his partner, 51-year-old accountant Lázaro “Lachi” González, work at the relatively mainline Evangelical Theological Seminary in Matanzas.
“God has no stepchildren, so we are all daughters and sons of God, and what Adiel and I do is have a life with love,” Lázaro González said.
The proposed law, which is to be considered by the National Assembly after the still unscheduled referendum, has more than 480 articles. It would also formally expand grandparents’ rights, allow for prenuptial agreements and —in cases of divorce— have financial consequences for those who have committed gender violence.
Parents could decide whether children’s paternal or maternal surname has precedence. Children’s rights would be gradually expanded as they grow.
But the biggest controversy is over changing the definition of marriage in the current law, which specifies it is between a man and a woman, to merely say between two people.
It would also open the way for gays to adopt, and for surrogate pregnancies —though not for payment.
“It is not going to bring any benefit,” said de Prada, general superintendent of the Assemblies of God, which have grown rapidly in Cuba and now claim more than 2,000 churches and one million members.
“The family, conceived as it is structured in the word of God, is that which is agreed between a man and a woman and the resulting children,” he said.
While Cuba was officially —and often militantly— atheist for decades after the 1959 revolution led by Fidel Castro, it has become more tolerant of religions over the past quarter-century. That has meant a greater opening not only for the once-dominant Roman Catholic Church, but also for Afro-Cuban religions, protestants, and Muslims.
Some of those churches took advantage of the opening in 2018 and 2019 to campaign against another plebiscite which would have rewritten the constitution in a way to allow gay marriage.
Opposition from social conservatives was strong enough that the government at that time backed away, though the change was backed by lawmaker Mariela Castro, daughter of then-President Raul Castro and director of Cuba’s Center for Sexual Education.
Justice Minister Oscar Silveira Martínez told the Associated Press that the new proposed law “does not construct social realities; it tries to foresee legal solutions, protect those social realities that exist.”
Assemblies of God General Secretary Julio César Sánchez said such unions would be “the result of sin.”
“The argument that they should be regularized because they exist is not valid,” he said, “because murder also exists. … That doesn’t mean it’s good.”
The differences play out in the streets as well.
“There are people who are going to be against same-sex couples joining in matrimony, but I think that’s something normal,” said Alberto Dausá, a 68-year-old retiree.
A few feet away, Carola Reyna, a 25-year-old housewife, said she wasn’t against gay couples being happy, “but it seems to me that [adopting] children, they shouldn’t get involved in that.”