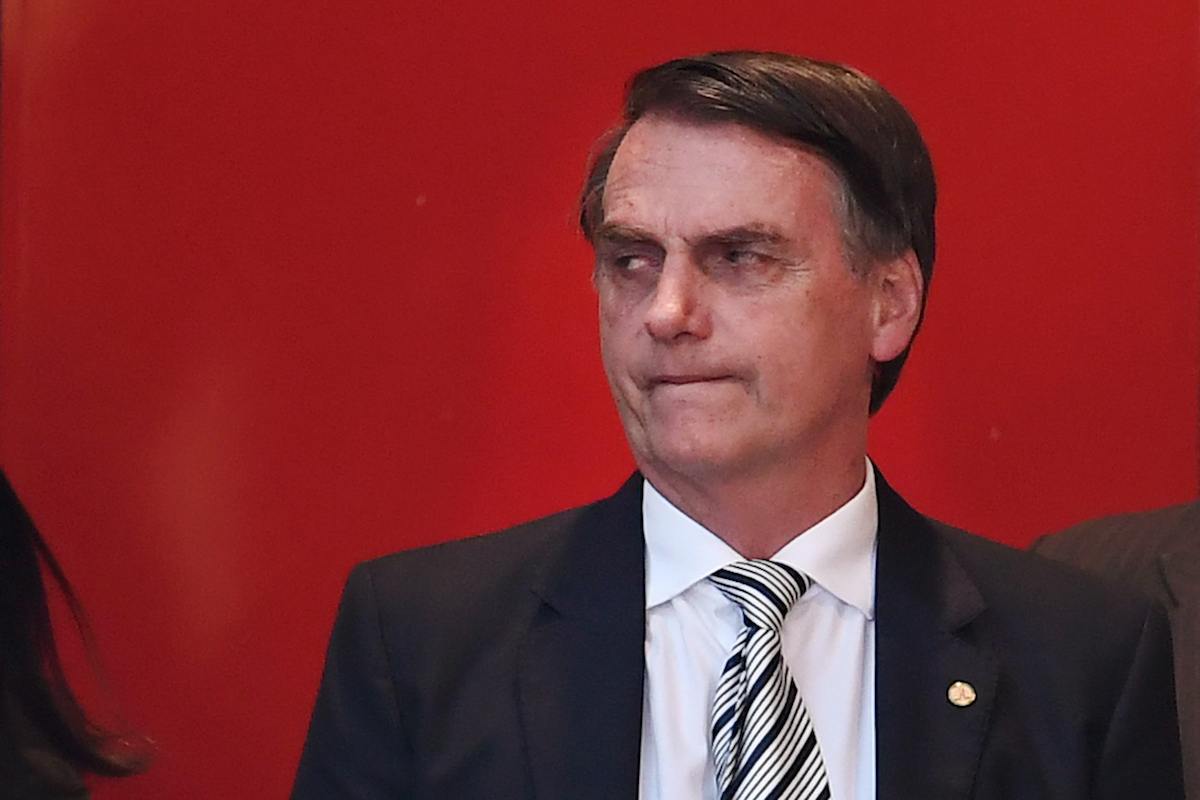
Brazilian President-elect Jair Bolsonaro gestures while leaving the transitional government headquarters in Brasilia, on December 4, 2018. (Photo by EVARISTO SA/AFP/Getty Images)
By Benjamin H. Bradlow, Brown University
Brazil’s next president Jair Bolsonaro, who takes power on January 1, is often called the “Trump of the Tropics” for his law-and-order rhetoric, racist and sexist remarks, pro-business stances and outsider pledges to upend politics as usual.
Bolsonaro also used a Trump-style populist playbook to win the Brazilian presidency in October with 54 percent of the vote. Spreading angry anti-establishment messages, he persuaded enough disaffected working-class voters to create a victorious if unusual electoral coalition of the working class and the very rich.
Unlike in the United States, however, where Trump targeted rural Americans left behind by economic progress, Bolsonaro’s working-class supporters mostly come from Brazilian cities—particularly the poor urban outskirts.
These areas, the focus of my sociology research on cities and democracy, has been hit hard by the severe crime wave and recession gripping Brazil since 2015, leaving a pool of precarious, disaffected voters ripe for Bolsonaro’s calls for radical change.
Brazil’s ‘New Middle Class’
Paradoxically, many of the working-class Brazilians who voted for Bolsonaro against his progressive opponent, Fernando Haddad, had seen their quality of life improve dramatically under Haddad’s center-left Workers Party.
These biggest gains occurred under President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva, who ran the country from 2003 to 2010. During his two terms, some 30 million poor Brazilians —15 percent of the population— were lifted out of poverty.
As incomes rose, working-class Brazilians began attending college, flying in airplanes and buying cars—luxuries previously reserved for the rich.
Ambitious slum-upgrading programs added sanitation systems, public transportation and electricity to long-overlooked urban shantytowns. Affordable housing subsidies put more people in safe, stable homes.
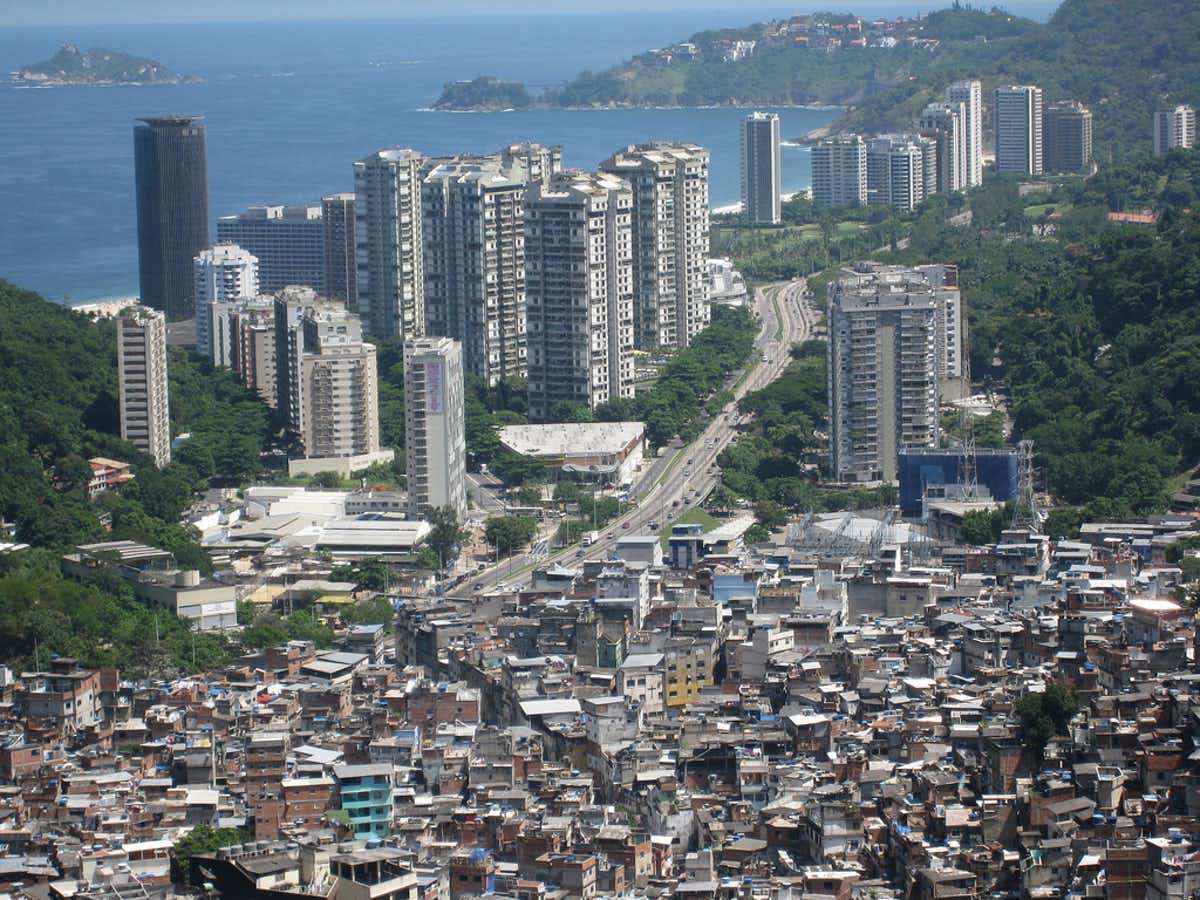


Rocinha, a large favela in Rio de Janeiro overlooking the wealthy São Conrado neighborhood. AHLN/flickr, CC BY
Brazil was celebrated worldwide as a South American star.
Lula’s anti-poverty achievements earned his Workers Party the fierce loyalty of poorer Brazilians. They voted overwhelmingly for his re-election in 2006 and supported his hand-picked successor, Dilma Rousseff, in Brazil’s 2010 and 2014 presidential elections.
But 2018 was different.
Bolsonaro won many working-class urban neighborhoods expected to go to his Workers Party opponent, Fernando Haddad. In São Paulo’s urban periphery, for example, Bolsonaro won 17 of the 23 electoral zones that voted overwhelmingly for Rousseff in the 2010 election.
Brazil’s Crime Wave
How did a far-right candidate attract left-wing voters?
New research from Brazil suggests that support for Bolsonaro among poorer Brazilians was driven in large part by high urban crime.
Brazil has had one of the world’s worst homicide rates for over a decade. On average, 175 Brazilians are murdered every day.
Poor urban neighborhoods are hot spots in this national crime wave. Turf wars between rival gangs and police shootouts terrorize Brazilians daily in the slum settlements and shantytowns that surround even Brazil’s richest cities.
Even in São Paulo, where homicides have actually decreased since 1999, frequent armed robberies, particularly car jackings, have residents feeling perpetually unsafe.
Bolsonaro’s crime-fighting plan is vague but forceful. It includes instructing police to “shoot to kill,” battling gangs and using the military as law enforcement.
Experts say this hard-line approach is unlikely to reduce violence. Brazilian law enforcement is already extremely aggressive, killing more often than any other police force worldwide. And sending soldiers in to “pacify” Rio de Janeiro’s favelas in 2017 actually increased shootings.
But coming from a former army captain like Bolsonaro, many Brazilians found the law-and-order messages comforting.
Recession, Crisis and a Backlash
Economic troubles have also left Brazilian workers feeling endangered.
In 2015, Brazil entered a severe recession. Gross domestic product – which since 2004 had averaged around 3 percent growth every year – shrank by 3.5 percent in both 2015 and 2016.
Unemployment doubled, to over 12 percent. One in 4 working-age Brazilians suddenly became “underemployed.”
The recession, coupled with a nationwide corruption scandal that had implicated many high-ranking government officials, including Lula, created a sense of political chaos. Brazil’s crisis only deepened after the 2016 impeachment of President Dilma Rousseff.
Rousseff’s successor —her vice president, Michel Temer— pushed through an austerity budget that gutted the social programs helping poor and working-class Brazilians.
Bolsonaro’s Big Promises
By January 2018, when the Brazilian presidential race began, it was clear that Brazil’s lauded “new middle class” had been hit hardest by the crisis.
Bolsonaro, who wants to reduce the government’s role in the Brazilian economy, had few economic promises for the poor—especially compared to the Workers Party’s phenomenal track record of redistributing wealth.
He made up for it by running a campaign of raw anger.
Bolsonaro pushed a narrative that Brazil’s recession was caused by corruption in the Workers Party, and he promised to clean up politics. He said criminals should die, lauded military dictatorships and proposed jailing leftists. He used racist, sexist and homophobic remarks to blame minorities and political correctness for Brazil’s decline.
Nearly 58 million voters —both rich and not-so-rich, black and white, homosexual and heterosexual— thought this bombastic authoritarian strongman might be just the man to get Brazil back on its feet.
Can Bolsonaro Help the Working Class?
Some political analysts reckon they bet wrong, saying Bolsonaro’s policy agenda will most likely hurt Brazil’s working classes.
A plan to auction off Brazil’s state electricity and oil companies to the highest bidder, for example, may give the economy a short-term boost, but economists warn that privatization won’t make these important sectors any more efficient or innovative.
His promise to shutter the Ministry of Cities, which oversaw Brazil’s federal slum-upgrading investments under Presidents Lula and Rousseff, will hobble poorer cities. Programs for housing, sanitation and transportation infrastructure are all under threat.
But that doesn’t mean urban working class voters will abandon Bolsonaro.
After all, Trump’s approval ratings in the United States among his white working-class base have been relatively durable despite a 2017 tax reform that primarily benefited the rich and tariffs that hurt key sectors of the American economy.
Bolsonaro used the tried-and-true playbook of authoritarians worldwide to win the Brazilian presidency. The resentments of gender and race that he stoked among poorer voters may continue to flourish even if these voters’ economic prospects do not.![]()
![]()
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.